2019
EuroSciCon CONFERENCE ON NANOTECHNOLOGY 2019, June 8-10, Prague, Czech Republic
Geanina Voicu1, Cristina Ana Constantinescu1,2, Daniela Rebleanu1, Agneta Simionescu3, Maya Simionescu1, Ileana Manduteanu1, Manuela Calin1
1Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology “Nicolae Simionescu”, Bucharest, Romania 2UASVM, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Bucharest, Romania3Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, United States of America
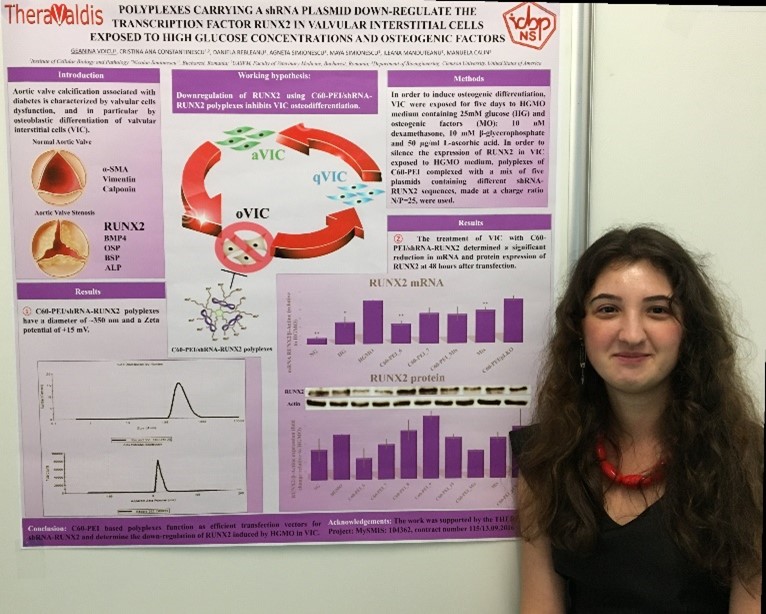
Introduction. Aortic valve calcification associated with diabetes is characterized by valvular cells dysfunction, and in particular by osteoblastic differentiation of valvular interstitial cells (VIC). Our previous results have shown that VIC exposed to media containing high glucose and osteogenic factors (HGMO) have an increased expression of proteins involved in VIC activation and osteodifferentiation. In this process, a major role is played by Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), which regulates the expression of genes involved in osteogenesis.
Purpose. To develop fullerene-PEI (C60-PEI) based polyplexes to function as nanocarriers for specific delivery of plasmids containing shRNA sequences specific for RUNX2 down-regulation in VIC.
Methods. In order to induce osteogenic differentiation, VIC were exposed for five days to HGMO medium containing 25mM glucose (HG) and osteogenic factors (MO): 10 nM dexamethasone, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate and 50 µg/ml L-ascorbic acid. In order to silence the expression of RUNX2 in VIC exposed to HGMO medium, polyplexes of C60-PEI complexed with a mix of five plasmids containing different shRNA-RUNX2 sequences, made at a charge ratio N/P=25, were used. The polyplexes were characterized for size and zeta potential. The efficiency of RUNX2 down-regulation was analysed by quantitative PCR and Western Blotting assay at 48 hours after transfection of VIC with C60-PEI/shRNA-RUNX2.
Results and Discussions. The mean diameter of polyplexes was around 350 nm with a zeta potential of +15mV. The treatment of VIC with C60-PEI/shRNA-RUNX2 determined a significant reduction in mRNA and protein expression of RUNX2 at 48 hours after transfection.
Conclusion. C60-PEI based polyplexes function as efficient transfection vectors for shRNA-RUNX2 and determine the down-regulation of RUNX2 induced by HGMO in VIC.
Acknowledgements. The work was supported by the THERAVALDIS Project: MySMIS: 104362, contract number 115/13.09.2016.